Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the IT sector has been a driving force behind global advancements. However, the rapid pace of technological change has not only brought about innovation but has also led to shifts in the job market, resulting in job losses in the IT industry. This article delves into the challenges faced by IT professionals in the wake of job losses and explores the potential opportunities that may arise amidst these changes.
In 2023, Forbes indicated that: Global employers anticipate creating 69 million new positions by 2027 and eradicating 83 million jobs—a net loss of 14 million roles. Clerical workers will bear the brunt of the fast-moving changes. Around 26 million jobs in administrative positions will be cut due to AI. Should this be a concern?
Number of tech employees laid off worldwide from 2020 to 2023, by company.
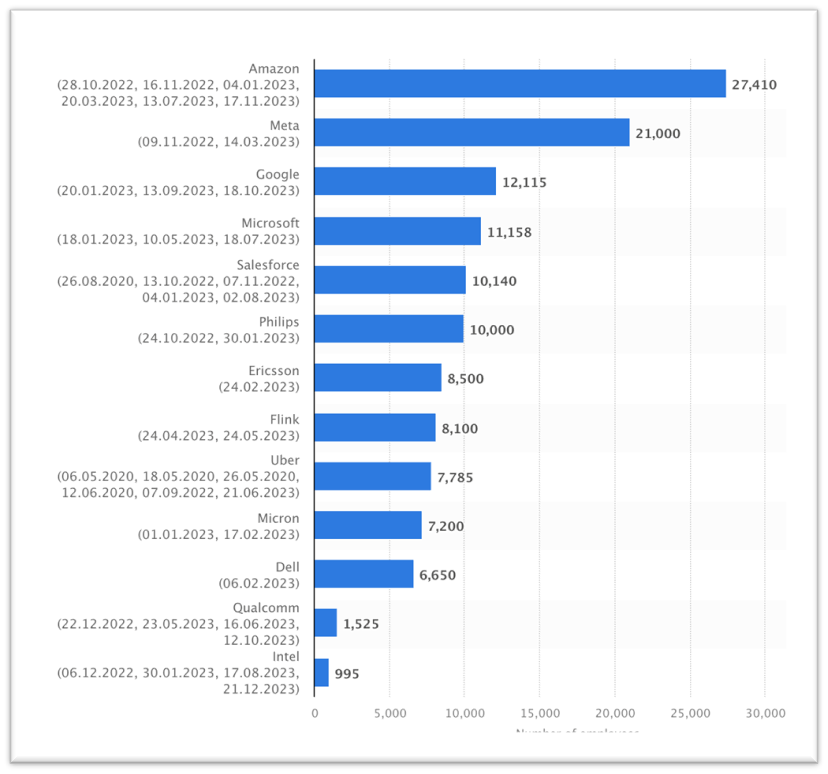
Source: Statistica.com
Major Causes of IT Job Losses
- The Impact of Automation and Artificial Intelligence
One of the primary drivers of IT job losses is the increasing integration of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) into various industries. Tasks that were once performed by humans are now being executed more efficiently and rapidly by machines. While this results in improved productivity and cost-effectiveness for businesses, it also translates to a reduced demand for certain IT roles.
- Outsourcing and Globalization
Globalization has opened up opportunities for companies to leverage talent from around the world, leading to the outsourcing of IT services. While this has undoubtedly expanded the reach of businesses and reduced operational costs, it has simultaneously contributed to job losses in high-cost regions. IT professionals in these regions often find themselves facing increased competition from their global counterparts.
- The Cloud Revolution
The widespread adoption of cloud computing has transformed the IT landscape. Cloud services offer scalability, flexibility, and cost savings for businesses, reducing the need for extensive in-house IT infrastructure and support. As a result, traditional IT roles related to server maintenance, system administration, and network management is experiencing a consistent decline.
Solutions to IT Job Losses
- Adapting to Change: Reskilling and Upskilling
In the face of IT job losses, the imperative for IT professionals is to adapt and stay relevant in the ever-changing industry. Reskilling and upskilling programs become crucial for individuals to acquire new skills demanded by emerging technologies. Professionals who can transition into roles that complement automation, such as AI development, cybersecurity, and data science, may find themselves in high demand.
- Entrepreneurship and Gig Economy
The changing landscape of IT job opportunities also opens avenues for entrepreneurship and participation in the gig economy. IT professionals can explore freelance and contract work, offering their expertise on a project basis. This shift towards a more flexible work model allows individuals to take greater control of their careers and find diverse opportunities beyond traditional employment structures.
- Government Initiatives and Policies
Governments and industry bodies play a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of IT job losses. Implementing policies that support retraining programs, fostering innovation, and incentivizing businesses to invest in human capital can help create a more resilient and adaptable workforce.
Below are some key findings of the World Economic Forum 2023
Source: WEF – Future of Jobs Report 2023
The impact of most technologies on jobs is expected to be a net positive over the next five years.
Big data analytics, climate change and environmental management technologies, and encryption and cybersecurity are expected to be the biggest drivers of job growth. Agriculture technologies, digital platforms and apps, e-commerce and digital trade, and AI are all expected to result in significant labour market disruption, with substantial proportions of companies forecasting job displacement in their organizations, offset by job growth elsewhere to result in a net positive. All but two technologies are expected to be net job creators in the next five years: humanoid robots and non-humanoid robots.
The fastest-declining roles relative to their size today are driven by technology and digitalization.
The majority of fastest declining roles are clerical or secretarial roles, with bank tellers and related clerks, postal service clerks, cashiers, ticket clerks, and data entry clerks expected to decline fastest.
The largest losses are expected in administrative roles and in traditional security, factory and commerce roles.
Surveyed organizations predict 26 million fewer jobs by 2027 in record-keeping and administrative roles, including cashiers, ticket clerks; data entry, accounting, bookkeeping, payroll clerks; and administrative and executive secretaries, driven mainly by digitalization and automation.
Employers estimate that 44% of workers’ skills will be disrupted in the next five years. Cognitive skills are reported to be growing in importance most quickly, reflecting the increasing importance of complex problem-solving in the workplace. Surveyed businesses report creative thinking to be growing in importance slightly more rapidly than analytical thinking. Technology literacy is the third-fastest growing core skill. Self-efficacy skills rank above working with others, in the rate of increase in importance of skills reported by businesses. The socio-emotional attitudes which businesses consider to be growing in importance most quickly are curiosity and lifelong learning; resilience, flexibility and agility; and motivation and self-awareness. Systems thinking, AI and big data, talent management, and service orientation and customer service complete the top 10 growing skills. While respondents judged no skills to be in net decline, sizable minorities of companies judge reading, writing and mathematics; global citizenship; sensory-processing abilities; manual dexterity, endurance, and precision to be of declining importance for their workers.
Analytical thinking and creative thinking remain the most important skills for workers in 2023.
Analytical thinking is considered a core skill by more companies than any other skill and constitutes, on average, 9% of the core skills reported by companies. Creative thinking, another cognitive skill, ranks second, ahead of three self-efficacy skills – resilience, flexibility and agility; motivation and self-awareness; and curiosity and lifelong learning – in recognition of the importance of workers ability to adapt to disrupted workplaces. Dependability and attention to detail, ranks sixth, behind technological literacy. The top 10 core skills are completed by two attitudes relating to working with others – empathy and active listening and leadership and social influence – as well as quality control.
Conclusion
While IT job losses are a challenging reality in today’s technology-driven world, they also present opportunities for growth, innovation, and personal development. The key lies in embracing change, acquiring new skills, and exploring diverse career paths. As the IT industry continues to evolve, individuals and organizations alike must collaborate to navigate the challenges and shape a future that maximizes the potential for both technological advancement and human prosperity.
Author: Emmanuel K. Gadasu, CEH, CDPS, CIPM, BSc IT, MSc IT and Law*, LLB* | Data Protection Officer, IIPGH | Data Privacy Consultant and Practitioner, Information Governance Solutions.
For comments, contact author via ekgadasu@gmail.com or Mobile: +233-243913077





