The use of Automated Teller Machine (ATM) cards or debit cards is on the rise as banking institutions have made it easier for all its customers to acquire ATM cards. Having the card has an advantage for the banking institution because customers do not put much pressure on the human workforce in the banking hall, but rather utilize the service of the ATM. According to Wikipedia, an ATM card is any payment card issued by a financial institution that enables a customer to access an ATM in order to perform transactions such as deposits, cash withdrawals, obtaining account statement, online transactions, etc.
Now let us delve deep into an aspect of the functions of the ATM card which is online banking. Online banking allows the card owner to perform banking services on the internet and engage in online transactions such as the payment of utility bills, shopping and online reservations which usually require the customer to make electronic payment on the internet. Life has become much easier because these actions can be done from any place in the world.
The use of ATM cards on the internet exposes the user to so many cyber-crimes such as identity theft. The banking system in Ghana has weak security controls and the entire online banking system does not provide security measures to protect the card owner in case a cyber-criminal intercepts the card owner’s online banking login credentials or steals the ATM card.
Vulnerabilities in the online banking system
The current online banking system in Ghana has no authentication processes. Authentication is the process of determining whether someone is who he/she declares to be. In Ghana, banking institutions do not verify the actual owner of the card before authorization is granted to online transactions. The danger is that if anyone gets access to the customer’s online banking login details or the ATM card, the person could easily have access to the card owners banking account.
For instance if a customer in Ghana, makes a hotel reservation online and then makes electronic payment, the bank will authorize payment immediately without asking the customer whether he is the one actually making the payment. This makes it extremely dangerous to use debit cards or ATM cards issued in Ghana to transact business on the internet. This is not so in other parts of the world such as US, UK, India, China, etc. These countries have strong online banking security features which always ask for the customer’s approval before any online payment could be authorized. The banking institution sends text message to the customer to approve the transaction; this action is done to confirm if the customer is actually the person performing the online business.
Once a cyber-criminal gets access to the customer’s online banking login details, all the money in the customer’s account could be withdrawn without his/her knowledge. Malicious persons or cyber criminals use many techniques to acquire information from the customer, especially login details. It has now become very easy for anybody including non-IT professionals to conduct criminal activities on the internet. These miscreants often download hacking tools from the internet to steal or intercept the credentials of customers online. Other malicious persons also use phishing scams. These scams are based on communication made via email or on social media networks. Cyber criminals mostly send messages (SMS or email) to their unsuspecting victims in order to trick them to give away sensitive information or login credentials such as bank account, social media account, debit card information or any other information that can prove to be useful or valuable, which will help the criminals to launch an attack on the victim.
ATM Card fraud
Almost all the banking institutions in Ghana issue either Visa or Master Cards. Each card has a specific or unique security feature such as the 16-digit card number and the 3-digit-code. When you turn your ATM card and look at the signature box, you should see either the entire 16-digit debit card number or just the last four digits and the special 3-digit code. This 3-digit code is the Card Verification Value/Code (CVV) number as indicated in the diagram below. CVV is an anti-fraud security feature which helps to verify that the card owner is the one using it.
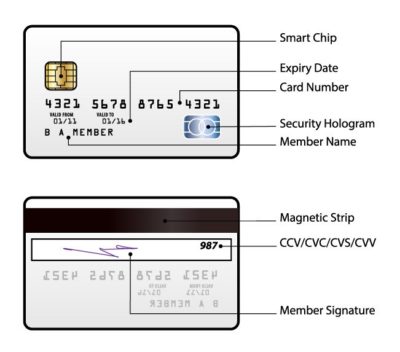
Should anyone get access to your CCV and your card number, the person can easily withdraw or transfer money from your account or perform online transactions without your knowledge. It is quite unfortunate that Bank of Ghana has allowed this security breaches to permeate deep into the banking system in Ghana. All banking institutions must introduce an appropriate card user authentication feature whereby each activity done with the card could be verified by the card owner before authorization could be granted.
The way forward
BOG must outline a suitable online banking authentication mechanism for all the banking institutions. The implementation of such mechanisms must ensure that an alert must be sent to the customer for any banking activity on his/her account. In this case, the customer or the bank could prevent or authorize withdrawal of money and online payments. The proposed solutions for this vulnerability are:
- Banks must be tasked to send text message alerts to the card owner, to authorize or deny any activity on the card
- The bank could ask the user some personal questions of the card owner, failure to provide correct answers shall obviously lead to the cancellation of the transaction
- The bank may also call the customer to verify if he/she is actually performing any transaction online before the bank grants authorization.
Conclusion
We are all at risk in Ghana. This is a serious matter and the banking regulatory body must rise to the task to ensure all banking institutions in the country implement some form of security measures to protect the customer. The country must not wait till the zero-day a big cyber disaster hit the banking industry, the solution has been provided so the designated authorities must ensure that the right security measures in the banking industry are implemented.
Author: Owusu Nyarko-Boateng, ICT Expert (Member: Institute of ICT Professionals, Ghana)
For comments, contact author: nbowusu7@gmail.com Mobile: +233244305305





